Parameter Estimation for Sound Synthesis
Main Contributors: Minsuk Choi
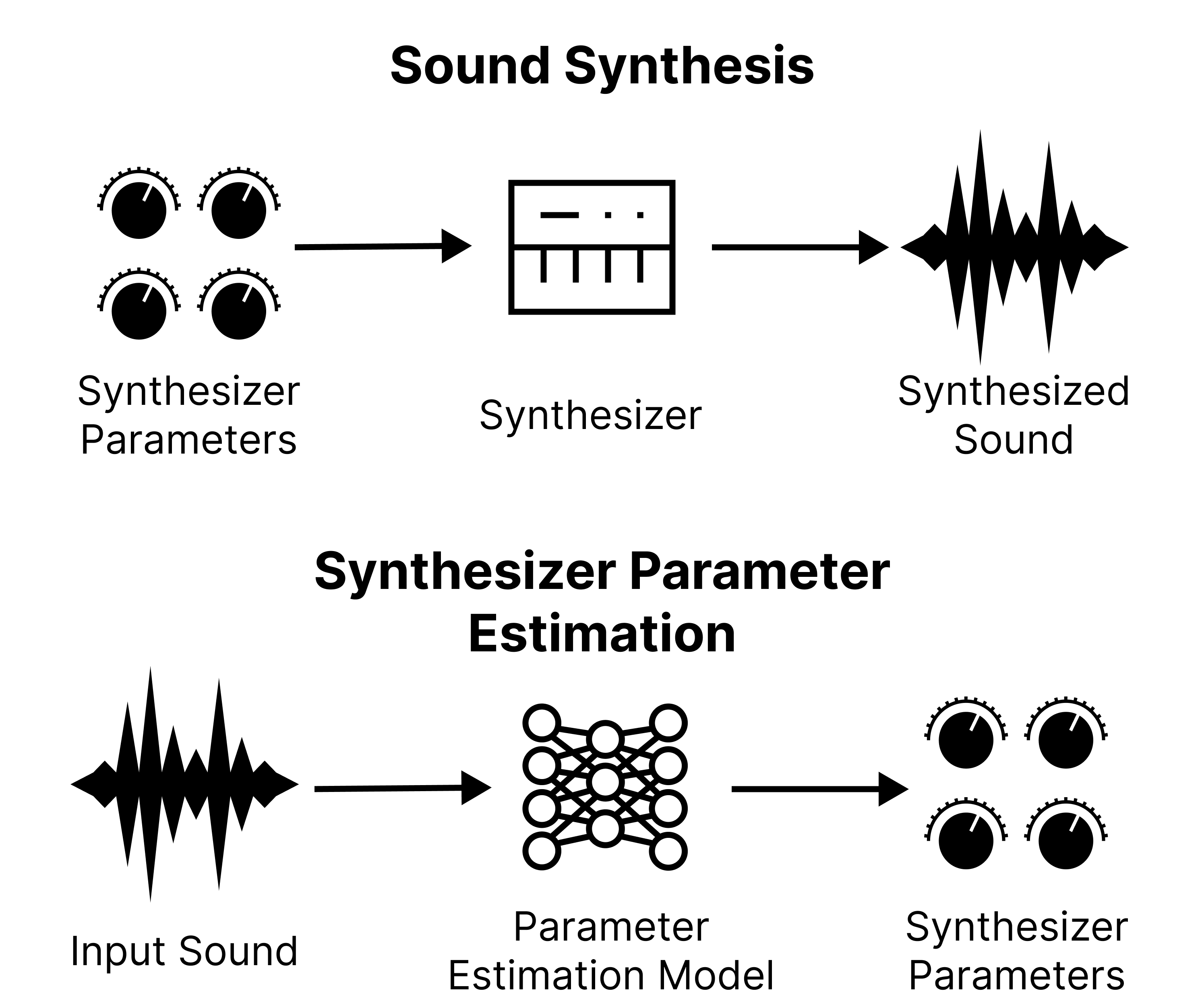
A synthesizer is a musical instrument that is capable of synthesizing various sounds from the sets of parameters. Synthesizer parameter estimation, or sound matching can be regarded as the inverse process of sound synthesis. It is a task to find a set of parameters that replicates the target sound as similar as possible. Finding corresponding parameters for the given target sound allows more controllability on modifying sounds and better understanding on sound designing. There are several points to consider to explore, define, and solve this task.
In-domain and Out-of-domain Target Sounds
Data can be distinguished in 2 types based on the availability of synthesizer parameters corresponding to target sounds.
In-domain sounds are the sounds that are synthesized by the target synthesizer, allowing the ground truth synthesizer parameters.
Additionally, the quantity and characteristics of data are controllable, meaning that we can synthesize sounds and augment dataset as needed.
However, the spectrum of data is limited to the expressive capability of the synthesizer.
Out-of-domain sounds are the sounds that are not related to the target synthesizer.
They are collected from various sources.
These sounds may possess characteristics that do not align with the target synthesizer, making it more challenging to reproduce them approximatively using the parameters of the target synthesizer.
Out-of-domain sounds are associated with handling data that goes beyond the expressive capabilities of the synthesizer.
Parametric and Spectral Loss
Typicalaly two types of loss are used to train the syntheizer parameter estimation model.
Parametric loss is calculated using the pair of estimated parameters and ground truth parameters, and it is exclusively applicable to in-domain sounds.
Spectral loss, on the other hand, is computed with the pair of spectrograms from the sound synthesized by estimated parameters and the target sound.
Parametric loss allows smooth optimization on in-domain sounds, but the model trained solely on parametric loss of in-domain sounds prone to making a poor estimation on out-of-domain sounds.
Spectral loss enables to use both in-domain and out-of-domain sounds for training, while having limitations on optimizing for certain types of parameters such as frequency.
Due to these trade-offs, parameteric loss and spectral loss can be employed complementarily, in various configurations of loss function and training scheme.
Differentiable Synthesizer
A differentiable synthesizer allows for the explicit utilization of synthesized sounds to train the model by propagating gradients from the loss computed using the output sounds. By using gradients explicitly, optimization become more stable. Proper and efficient implementation of diverse synthesizer modules enhances the spectrum of sounds and expressive capability of the model.
