Symbolic Music Similarity
Main Contributors: Saebyul Park
Melody Similariy and Copyright Infringement
This study aims to objectively measure melody similarity in music copyright infringement cases using natural language processing (NLP) techniques. The approach includes the following steps:
- Implementing Mel2word: A melody tokenization technique for semantic analysis, converting melodies into word-like units
- Applying Word Embedding with Weighting : Utilizing a modified Tversky measure and TF-IDF to evaluate substantial similarity, enhancing the distinction between original and infringing works.
- Compiling the Music Copyright Infringement Collection (MCIC): A dataset of 116 cases transcribed into MIDI data with relevant metadata.
Our primary focus is to define word-like elements of melody using NLP methods. To achieve this, we employ Mel2word, a novel technique that converts melodies into word-like units suitable for semantic analysis through word embeddings.

Mel2Word: A BPE-based Text Representation for Melody for NLP Analysis
To evaluate the distinctive features of a melody, we propose two methods drawn from the fields of psychology and NLP. The modified Tversky measure assesses word salience, determining how prominent or distinct a melodic element is. TF-IDF evaluates the importance and uniqueness of each word-like unit, capturing how significant and rare it is across the dataset.
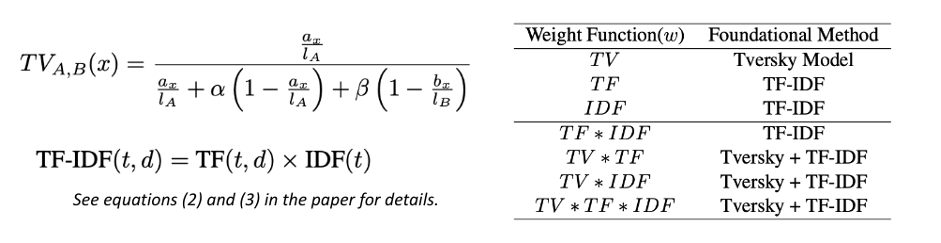
Summary of Weight Functions
For our empirical investigation, we compiled the MCIC, which includes scores, legal decisions, and case summaries. We validated our method on 108 plagiarism cases by comparing Mel2word-based song vectors to court decisions, using Word2Vec with cosine similarity to assess alignment with both court rulings and perceptual similarity. The results demonstrate that our approach outperforms traditional methods.
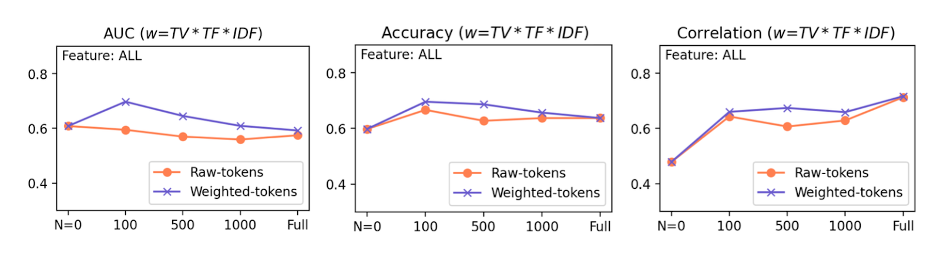
Summary of results with various dictionaries and weight presence.
The strength of our method lies in its numerical representation of melodic elements, allowing us to observe values for importance, uniqueness, and salience. This enhances our understanding of which parts significantly contribute to similarity.
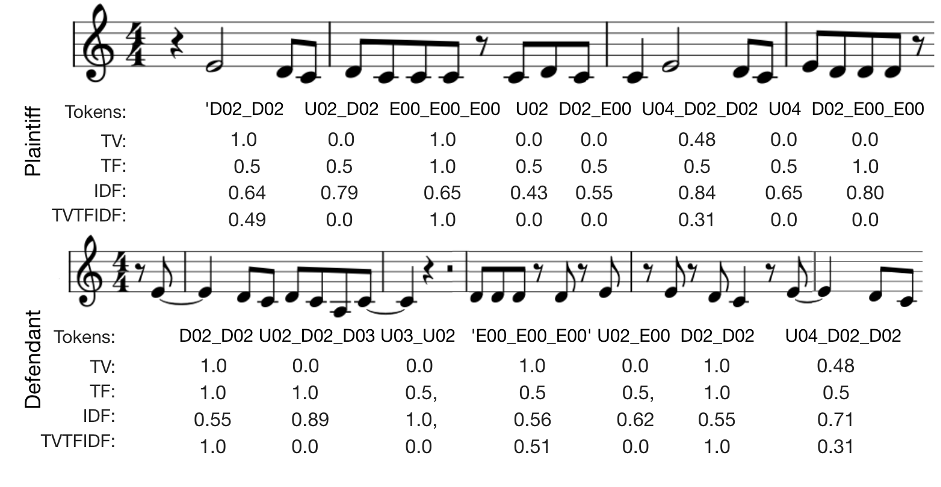
An example of melody weighting values (Three Boys Music v. Michael Bolton)
The cross-scape plot indicates that darker areas represent higher similarity, providing a quantitative basis for both theoretical aspects of melodic similarity and practical issues like legal decisions.
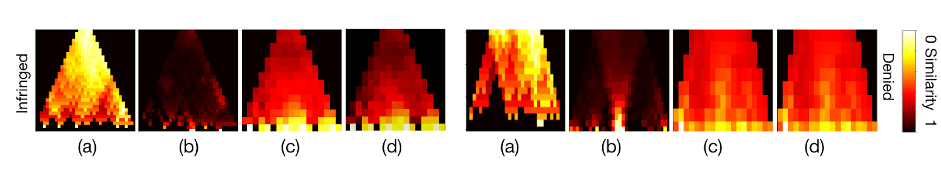
Cross-scape plots—(a) Original (Edit Distance), (b) Word2Vec morpheme, (c) Word2Vec token (no weights), (d) Word2Vec token (TVTFIDF)
For further information, see the research paper (ISMIR2024) linked below.
Related Publications
-
Quantitative Analysis of Melodic Similarity in Music Copyright Infringement Cases
Saebyul Park, Halla Kim, Jiye Jung, Juyong Park, Jeounghoon Kim, and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the 25th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), 2024
-
Mel2Word: A Text-based Melody Representation for Symbolic Music Analysis
Saebyul Park, Eunjin Choi, Jeounghoon Kim and Juhan Nam
Music and Science, 2024 [paper] -
The Language of Jazz: A Natural Language Processing-based Analysis of the Patterns and Vocabulary of Jazz Solo Improvisation
Saebyul Park and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Music Perception and Cognition (ICMPC), 2023 [paper]
Symbolic Melody Similariy Visualization
Melodic similarity is a key concept that helps with analysis and understanding in theoretical areas such as musicology, music cognition, and music psychology, as well as in applied areas such as music copyright, music classification and recommendation, and various fields. The process of determining melodic similarity is inherently intuitive and subjective. Psychological approaches to evaluating melodic similarity have relied on cognitive experimental evaluations, expertise, or music theory-based models, while computational methods derived from natural language processing have generally provided a single value. These fragmented approaches may only reveal task-specific information. Thus, our study aims to develop a comprehensive framework for quantitatively measuring the subjective and qualitative aspects of melodic similarity. To this end, we propose a novel method for evaluating the symbolic melodic similarity between two songs using multi-segment analysis of melodic sequences as well as visually inspecting cross-scape plots, which can compare two songs regardless of the location or length of similar phrases.
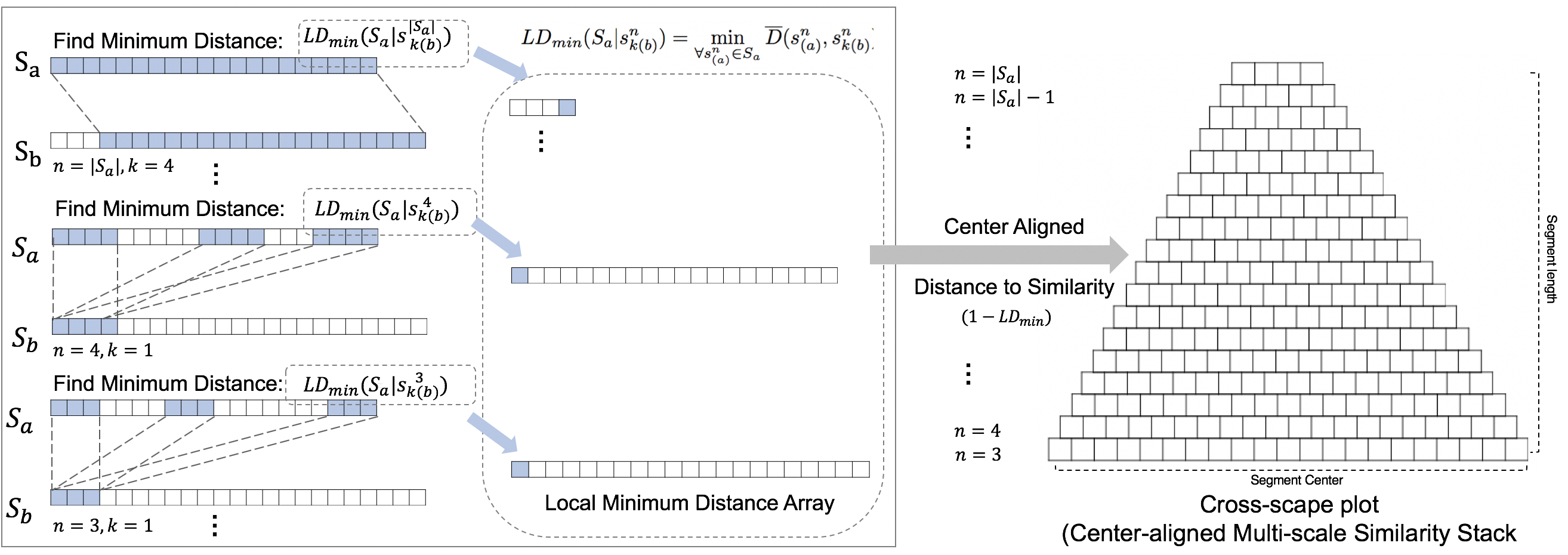
An Illustration of Steps for Drawing a Cross-scape Plot for Symbolic Melody Similarity
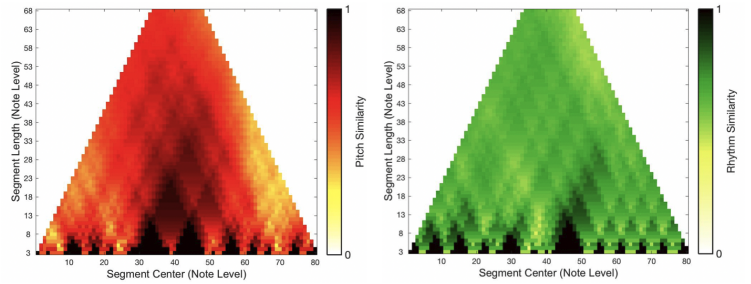
An example of a cross-scape plot by comparing similarities between two songs. The pixel value and the density of the color indicate the similarity score between the two sub-sequences.
The analysis procedure is summarized as follows: 1) Two songs are each segmented into all possible unit lengths, from the shortest to the longest. 2) A minimum local distance matrix between the two songs is constructed for all unit lengths. 3) The overall similarity measure is calculated by analyzing the cross-scape plots obtained by stacking up the local similarities. (Refer to the figures above.)
This hierarchical representation allows for capturing the location and length of similar segments between two songs in a visually intuitive manner. In our experimental research, we also showed the effectiveness of the cross-scape plot by evaluating it on examples from folk music collections with similarity-based categories and plagiarism cases. For further information, see the research paper linked below.
Related Publications
-
A Cross-Scape Plot Representation for Visualizing Symbolic Melodic Similarity
Saebyul Park, Taegyun Kwon, Jongpil Lee, Jeounghoon Kim, and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the 20th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), 2019 [paper] [code]
