Multimodal Music Retrieval
Main Contributors: Seungheon Doh
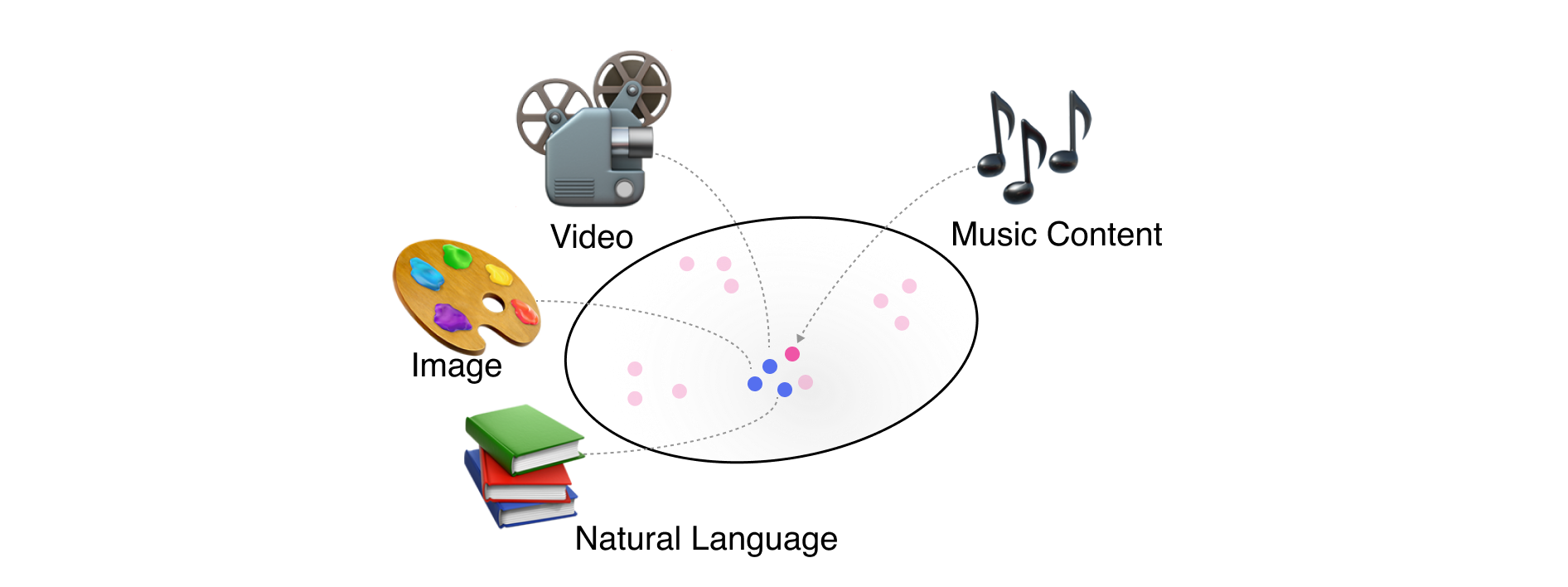
In the ever-evolving world of music streaming, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning has opened new horizons for user experience, particularly in the domain of multimodal music retrieval. This is searching for music through text, audio, and vision that have an association with music. This innovative approach goes beyond traditional methods, offering a more intuitive and interactive way for users to discover music.
Music and Text
One of the most fascinating aspects of multimodal music retrieval is the text-to-music feature. This technology allows users to find music based on text inputs, which can range from a single word to complex sentences. The system's ability to comprehend the semantic meaning of these inputs is crucial. For instance, when a user inputs a mood, a genre, or specific lyrics, the AI analyzes this data to present songs that closely match the described attributes.
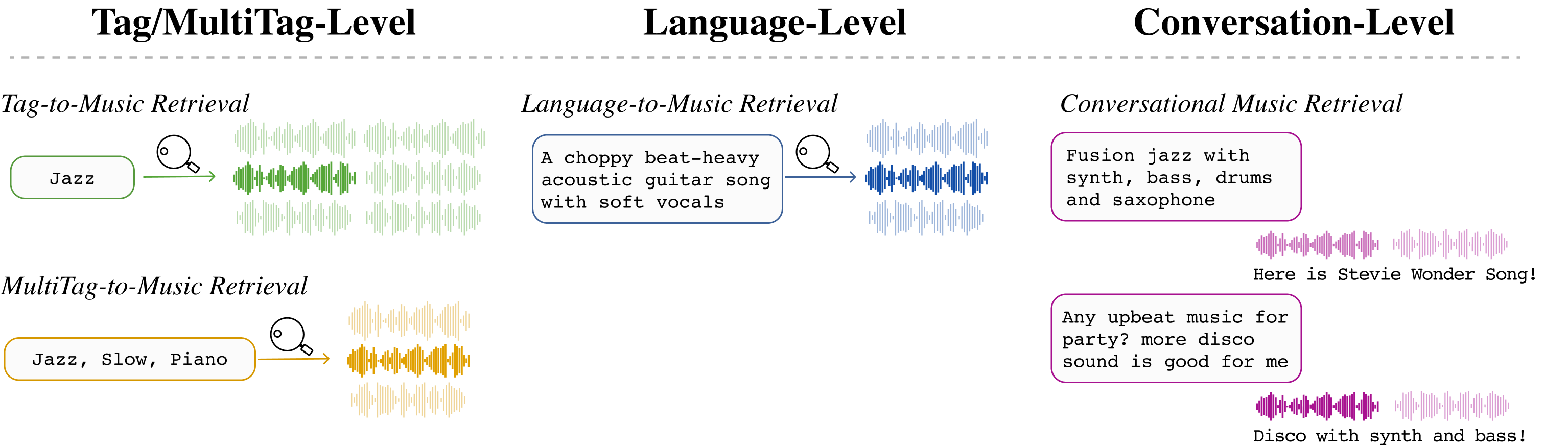
Another vital component in multimodal music retrieval is the understanding and utilization of metadata related to artists and tracks. Metadata includes information like the genre, release year, artist's background, and even the instruments used in a track. By analyzing this metadata, the AI can make more accurate recommendations, aligning with the user's preferences and past listening history.
Related Publications
-
Music Discovery Dialogue Generation Using Human Intent Analysis and Large Language Model
Seungheon Doh, Keunwoo Choi, Daeyong Kwon, Taesoo Kim, and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the 25th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), 2024 [paper] -
Enriching Music Descriptions with a Finetuned-LLM and Metadata for Text-to-Music Retrieval
SeungHeon Doh, Minhee Lee, Dasaem Jeong, Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2024 [paper] [website] -
The Song Describer Dataset: a Corpus of Audio Captions for Music-and-Language Evaluation
Ilaria Manco, Benno Weck, SeungHeon Doh, Minz Won, Yixiao Zhang, Dmitry Bodganov, Yusong Wu, Ke Chen, Philip Tovstogan, Emmanouil Benetos, Elio Quinton, György Fazekas, and Juhan Nam
Workshop on Machine Learning for Audio, Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2023 [paper] -
Toward Universal Text-to-Music Retrieval
Seungheon Doh, Minz Won, Keunwoo Choi, and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2023 [paper] [website] -
Million Song Search: Web Interface for Semantic Music Search Using Musical Word Embedding
Seungheon Doh, Jongpil Lee, and Juhan Nam
Late Breaking Demo in the 22st International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), 2021 -
Musical Word Embedding: Bridging the Gap between Listening Contexts and Music
Seungheon Doh, Jongpil Lee, Tae Hong Park, and Juhan Nam
Machine Learning for Media Discovery Workshop, International Conference on Machine Learning (ICML), 2020 [paper] [website] -
Zero-shot Learning for Audio-based Music Classification and Tagging
Jeong Choi, Jongpil Lee, Jiyoung Park, and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the 20th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), 2019 [paper] [code]
Music and Audio
the audio-to-music feature designed primarily for content creators. This innovative tool transcends the traditional text-based interfaces, leveraging the rich, textless audio modalities to recommend music that aligns with the emotional nuances in actors' voices.
The core concept of this technology is rooted in the understanding that human speech carries a wealth of information beyond mere words. Emotions, intonations, and subtle vocal inflections, often lost in text, are pivotal in conveying a story's essence. By analyzing these elements, the audio-to-music feature can suggest musical compositions that resonate with the underlying emotions of spoken dialogues. This harmony between speech and music amplifies the storytelling impact, offering creators a powerful tool to enhance their narrative.
Looking ahead, the potential applications of this technology are vast, especially in the realm of emotional Human-Computer Interaction (HCI). The ability to interpret and respond to emotional cues in human speech can revolutionize HCI, making interactions more intuitive, empathetic, and effective. This evolution signifies a shift from the conventional, text-dominated interfaces to more holistic, emotion-aware systems.
Related Publications
-
Textless Speech-to-Music Retrieval Using Emotion Similarity
Seungheon Doh, Minz Won, Keunwoo Choi, and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2023 [paper] -
Hi, KIA: A Speech Emotion Recognition Dataset for Wake-Up Words
Taesu Kim, SeungHeon Doh, Gyunpyo Lee, Hyung seok Jun, Juhan Nam, and Hyeon-Jeong Suk
Proceedings of the 14th Asia Pacific Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA), 2022 [paper]
Music and Vision (Stopped Project)
The ability to imagine images while listening to music is not just a testament to human creativity, but it also holds practical applications in areas like image-based music search and music visualization. This skill intertwines the auditory and visual senses, enabling a unique interaction between music and imagery, where music can evoke vivid visual scenes and, conversely, images can inspire musical compositions. It's a fascinating interplay that showcases the symbiotic relationship between sound and sight in artistic expression.
Related Publications
-
TräumerAI: Dreaming Music with StyleGAN
Dasaem Jeong, Seungheon Doh, and Taegyun Kwon
Workshop on Machine Learning for Creativity and Design, Neural Information Processing Systems (NeurIPS), 2020 [paper]
