AI DJ
Main Contributor: Taejun Kim
Once upon a time, humans found how to record music, and during the "Great Depression" radio stations started to play records instead of live musicians. Despite musicians’ resistance, playing records became standard way for radio. Soon, people started dancing with records in clubs instead of live music. Recorded music is not only a cheap way to listen to music, but it also has its own unique charm: music with various styles can be played.
Nowadays, dancing to recorded music led by DJs is a popular format in dance culture, however, it has never been explored thoroughly how DJs play music in a data-driven way, and use knowledge from statistical analysis to build a automatic DJ system.
The AI DJ project collected music records and DJ mixes that DJs played in the past shows (e.g. dance festivals and podcasts) in a large-scale. Our goal is to understand patterns in DJ techniques and use the distilled knowledge to build automatic DJ systems which can help human DJs and listeners.
DJ Mix Analysis
The DJ mix analysis has a goal of understanding patterns in DJ techniques statistically of which questions can be such as:- How do they select music records? Are genres/moods of the records consistent? Do they consider keys of the records?
- In which order do they play music?
- How much tempo/key modifications do they make for seamless flow of music while not hurting the original essence of individual records?
- How do they make a smooth transition from the previous to the next track?
- How do they control DJ mixers?
- Do they consider musical structures?
- ...and more!
- Track Identification recognizes which musical tracks are played by DJs.
- Mix-To-Track Alignment aligns the identified original tracks to the DJ mixes for further analysis.
- Cue Point Extraction finds time positions that the tracks start/end to be played in the DJ mixes.
- Transition Analysis explains which and how audio effects are applied to the previous and the next tracks for a smooth transition.
Mix-To-Track Alignment
The video below explains a mix-to-track alignment method using dynamic time warping (DTW) and statistical analysis of DJ mixes.Transition Analysis
The web demo below demonstrates transition analysis results, which explain how the DJ controlled EQ knobs on a DJ mixer. You can listen to individual EQ-applied tracks and reconstructed mix, and compare them to the original DJ mix. The video below details the motivation and results of the transition analysis.Related Publications
-
Joint Estimation of Fader and Equalizer Gains of DJ Mixers using Convex Optimization
Taejun Kim, Yi-Hsuan Yang, and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the International Conference on Digital Audio Effects (DAFx), 2022 [pdf] [dataset] [code] [slides] -
Reverse-Engineering The Transition Regions of Real-World DJ Mixes using Sub-band
Analysis with Convex Optimization
Taejun Kim, Yi-Hsuan Yang, and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the New Interfaces for Musical Expression (NIME), 2021 [paper] [code] [demo] [video] -
A Computational Analysis of Real-World DJ Mixes using Mix-To-Track Subsequence Alignment
Taejun Kim, Minsuk Choi, Evan Sacks, Yi-Hsuan Yang, and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the 21st International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), 2020 [paper] [code] [poster] [video]
Automatic DJ System
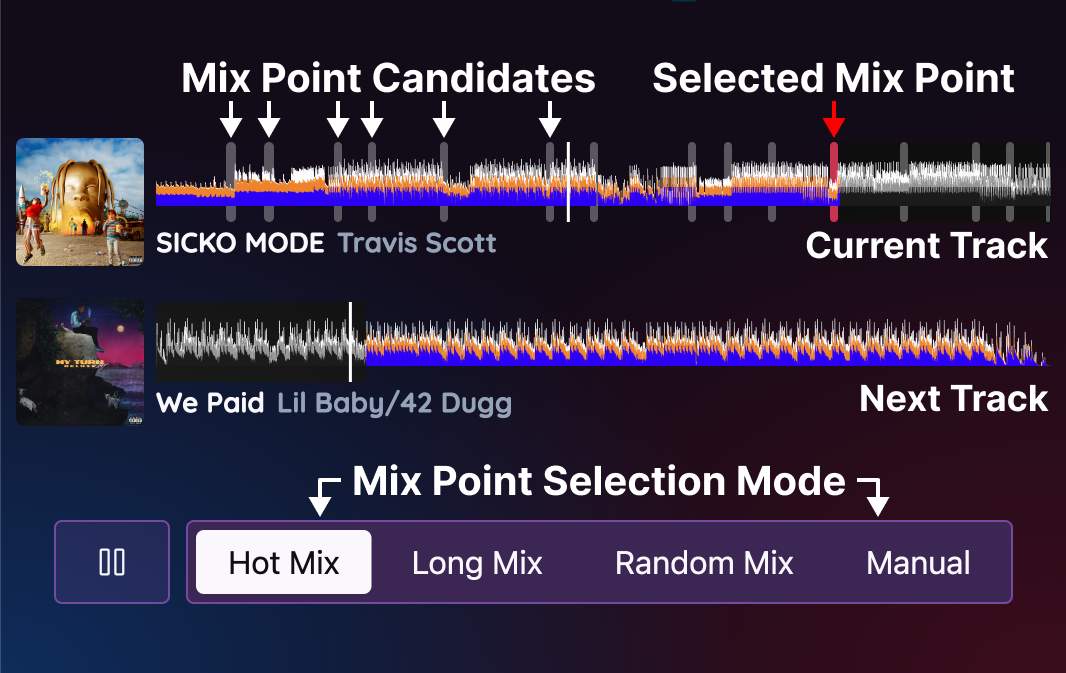
The creative process of DJing can be summarized as three steps making decisions of:
- What to play: selecting which songs to play
- Where to mix: deciding where to mix two adjacent songs
- How to mix: applying audio effects to make a smooth transition
- Step 1: music recommendation
- Step 2: cue point estimation
- Step 3: automatic DJ mixing
Structure Analysis
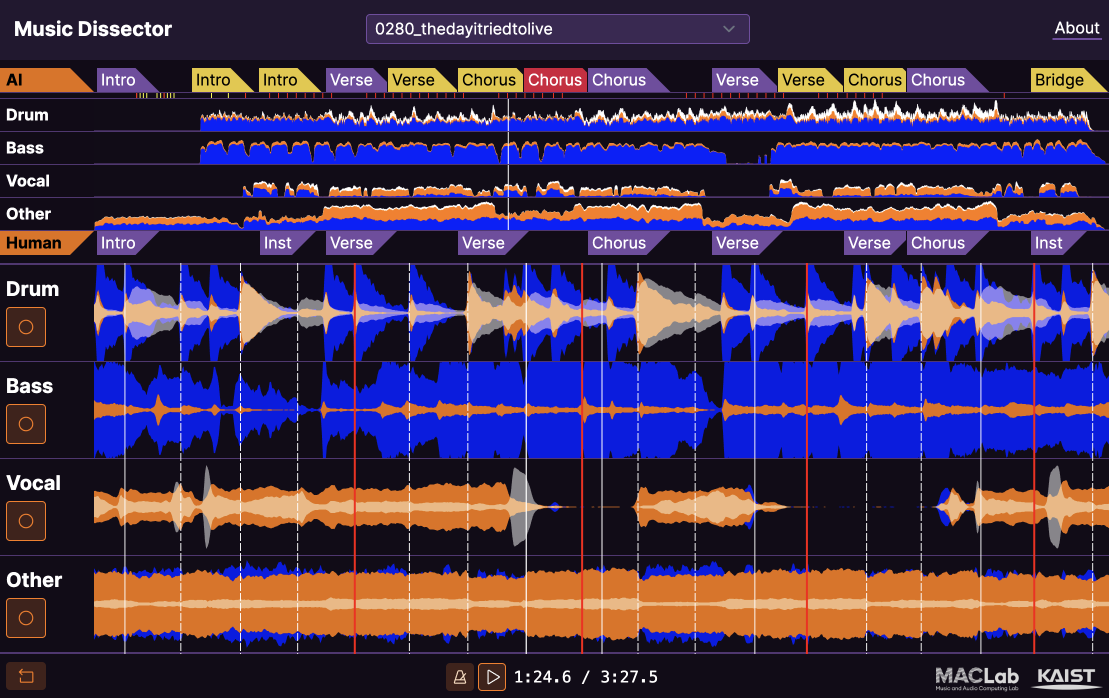
Understanding music structures is an essential skill for DJs, since the boundaries between sections (e.g., intro, verse, chorus) can serve as candidates for cue points. The interactive web demo below, Music Dissector, visualizes music structures analyzed by our structure analysis model.
DJ StructFreak
DJ StructFreak is an automatic DJ system that automatically selects songs based on music structures and let users select cue points freely.
Related Publications
-
DJ StructFreak: automatic DJ system built with Music Structure Embeddings
Taejun Kim and Juhan Nam
Late Breaking Demo in the 24th International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), 2023 [paper][video] -
All-In-One Metrical And Functional Structure Analysis With Neighborhood Attentions on Demixed Audio
Taejun Kim and Juhan Nam
IEEE Workshop on Applications of Signal Processing to Audio and Acoustics (WASPAA), 2023 [pdf] [python package] [ai dj demo] [visual demo] [hugging face space]