Real-Time and Audio-Visual Music Transcription
Main Contributors: Taegyun Kwon, Yonghyun Kim, Joonhyung Bae, Hyemi Kim
Transcripiton generally refers to the interpretation of music audio on a note-by-note basis, transforming it into a more easily readable and standardized format, such as sheet music or MIDI. The converted format can be utilized for understanding the music and performance, applications for playing music, or as data for learning. We explore transcriptions in various conditions, including real-time transcription, transcription for multiple instruments, and transcription with visual information.
Transcripiton Demo of Schubert Sonata (Avdeveva & Sokolov)
Real-Time Transcription
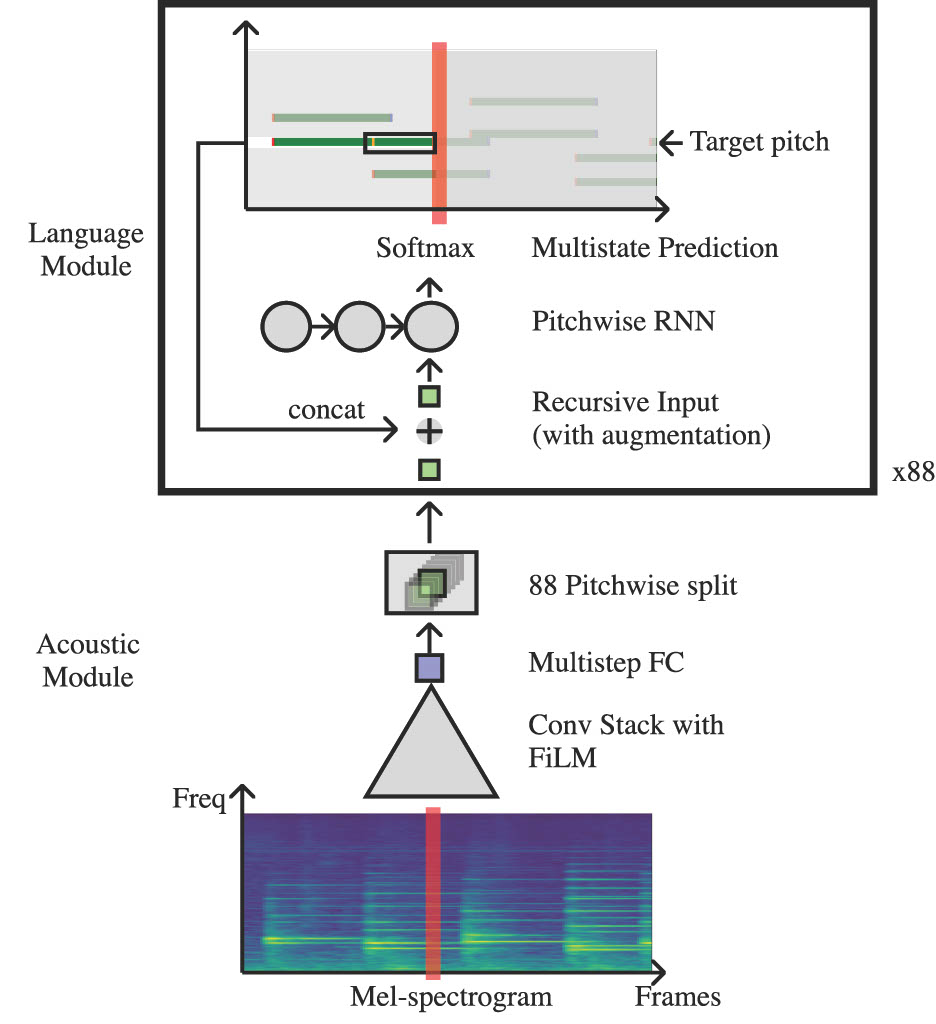
Deep learning networks for automatic piano sheet music transcription are generally not well-suited for real-time scoring when using bidirectional architectures. We propose a structure suitable for real-time processing by utilizing an autoregressive unidirectional network. We have further enhanced performance by incorporating musical features, including invariance to pitch changes.
Transcription Model Overview
With a real-time processing score model featuring a 320-millisecond delay, we achieved performance metrics of 97.0% and 87.9% for Note Onset and Offset F1 scores, respectively, on the MAESTRO dataset.
Realtime Transcripiton Demo (The delay is compensated on the main screen)
Related Publications
-
Towards Efficient and Real-Time Piano Transcription Using Neural Autoregressive Models
Taegyun Kwon, Dasaem Jeong, and Juhan Nam
IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio, Speech and Language Processing [paper] -
A Study of Audio Mixing Methods for Piano Transcription in Violin-Piano Ensembles
Hyemi Kim, Jiyun Park, Taegyun Kwon, Dasaem Jeong, and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), 2023
[paper] -
Polyphonic Piano Transcription Using Autoregressive Multi-State Note Model
Taegyun Kwon, Dasaem Jeong, and Juhan Nam
Proceedings of the 21st International Society for Music Information Retrieval Conference (ISMIR), 2020 [paper]
Audio-Visual Transcription
Humans encounter the world through various senses, such as vision, hearing, smell, and touch. (The world in which humans live is a multimodal environment.) Multimodality can also be applied in music analysis, particularly Automatic Music Transcription (AMT), where symbolic representation is obtained from performance audio.
In general, the environment for playing the piano is highly diverse, and the diversity of room/mic impulse responses and the presence of environmental sound are inevitable. In such situations, when choreographing, we explore how the visual input of piano performance can positively influence the music transcription results.
Piano Performance Audio-Visual Data Acquisition System Demo